Dealing with unwanted hair loss can be an incredibly frustrating and distressing experience, often accompanied by feelings of embarrassment. While it may be considered a cosmetic concern, societal norms surrounding long and lustrous hair for women can make hair loss particularly challenging to accept. In many cases, hair loss in women is linked to hormonal changes. However, there are numerous hidden causes of hair loss in women that frequently go unnoticed or unaddressed.
Female Pattern Hair Loss
Female pattern hair loss stands as one of the primary causes behind hair loss in women, affecting approximately one-third of the female population due to genetic predisposition. This condition can manifest at any point from puberty to menopause, initially leading to a gradual thinning of the hair. The root cause of female pattern hair loss lies in the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is present in both men and women. Excessive levels of DHT can trigger hair loss, contributing to the progression of this condition.
An Autoimmune Condition
Hair loss can be attributed to an autoimmune disorder called alopecia areata, wherein the body’s immune cells mistakenly target and attack its own cells. This condition leads to the formation of patchy areas of hair loss as the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
(PCOS) is linked to various health issues in women, and hair loss is one of them. This condition disrupts the balance of female hormones, leading to an excess production of testosterone by the ovaries. The elevated levels of testosterone can result in excessive body hair growth and hair loss in women affected by PCOS.
Medication
Hair loss can often be observed as a side effect of various medications, including antidepressants, beta-blockers, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Fortunately, in many cases, addressing the underlying cause and adjusting medication can help halt or even reverse the hair loss. By making changes to the prescribed medications, individuals experiencing this side effect may find relief and improvements in their hair growth.
Speak to your health professional about your options.
Hormones
The hormonal fluctuations that occur during pregnancy can bring about significant changes in a woman’s body. Hair loss is a common occurrence during various stages of pregnancy. In many cases, women may notice hair loss shortly after giving birth, as the body undergoes further hormonal adjustments. These postpartum hormonal changes can contribute to hair loss in new mothers.
Nourishing herbs
Saw palmetto and ginkgo biloba are known to have potential benefits in enhancing hair density. In a study where researchers incorporated saw palmetto extract into lotions and shampoos for a duration of three months, they observed that 35% of participants experienced an increase in hair density. Ginkgo biloba, on the other hand, has been found to promote blood circulation and provide antioxidant support to the body, contributing to stronger hair.
Balancing hormones
Imbalances in hormones can contribute to hair thinning. Including hormone-balancing foods in your regular diet can help regulate hormone levels and promote healthier hair. Consider incorporating foods like avocados, nuts, pomegranates, organic apples, and chia seeds into your meals to support hormonal equilibrium and potentially address hair thinning concerns.
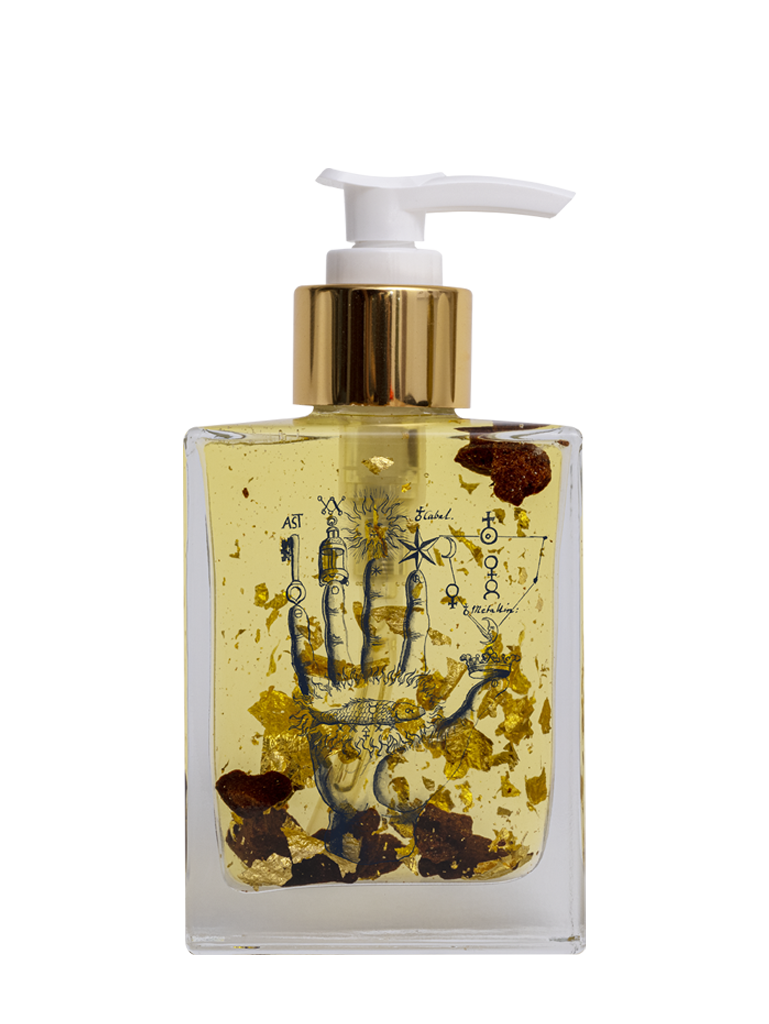
Oil therapy
Research has indicated that rosemary oil and castor oil can be an effective topical treatment for hair loss. It possesses properties that can enhance cellular metabolism and stimulate hair growth. Additionally, combining peppermint oil and sage oil may help combat hair thinning. Consider exploring these natural remedies to potentially address hair loss concerns.
Check out our crown oil with all these ingredients.






 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart. 